Welcome back to our series on understanding the components of your windows and doors! In this article, we’ll explore the wide array of glass options available for your windows and how each type contributes to energy efficiency, safety, UV protection, privacy, and aesthetics. By the end, you’ll have the insights needed to make an informed choice for your home.
Understanding Glass Coatings and Surfaces
Before diving into specific glass options, it’s important to understand the concept of glazing surfaces and how they affect the performance of your windows. In insulated glass units, each pane of glass has multiple surfaces, numbered from the exterior to the interior. For instance:
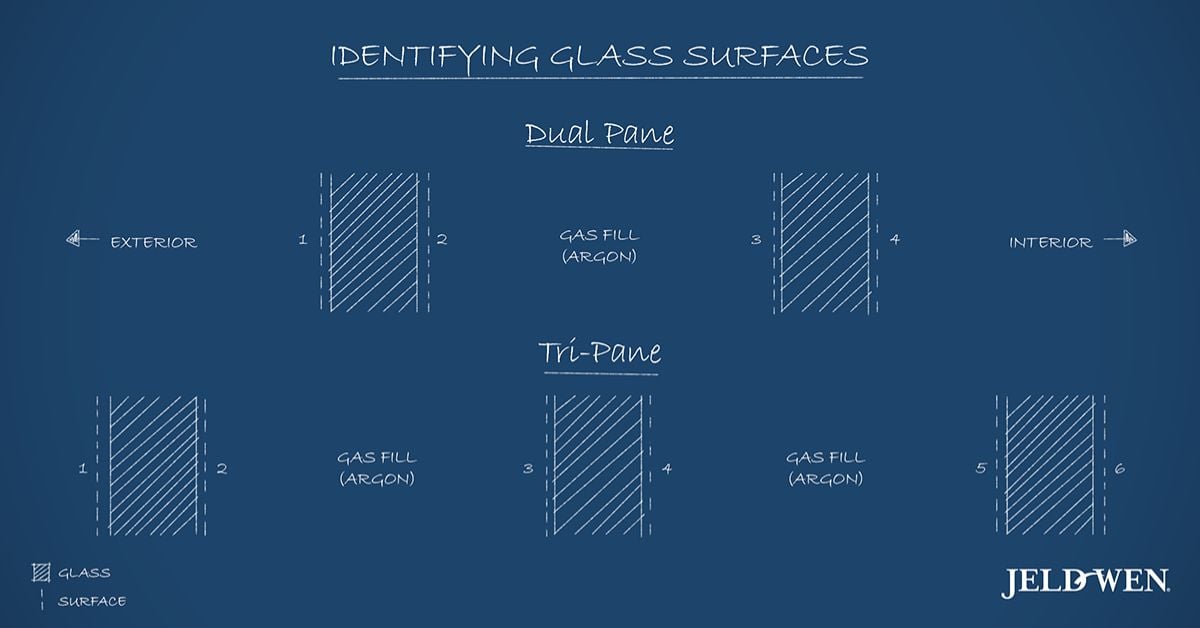
These surfaces play a crucial role in determining the placement of Low-E coatings and other treatments, influencing energy efficiency, UV protection, and light transmission.
Visible Transmittance (VT) is another critical factor to consider. VT measures how much natural light passes through the glass, rated on a scale from 0 to 1. Higher VT values allow more light into your home, which is ideal for colder climates, while lower VT values help reduce glare and heat in warmer regions.
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork, let’s explore the various glass options and their benefits.

Types of Glass and Their Benefits
Low-E Glass: Energy Efficiency at Its Best
Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass features a special coating that reflects heat while allowing natural light to pass through. Depending on where the coating is applied—on different glazing surfaces—the performance can be tailored to your climate needs.
Key Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: Reflects indoor heat back into the room during winter and keeps outdoor heat out in summer.
- UV Protection: Blocks harmful UV rays, reducing sun damage to furniture and flooring.
- Versatility: Available in single, double, or triple coatings for varying climates.
Options to Consider
SunFlow™ Low-E Glass
Ideal for colder regions, it allows passive solar heating while blocking 55% of UV rays.
Dual Pane: (VT: 0.66*)
- DF/UW: 1 Coating on surface 3
- WW: 1 Coating on surface 2
Tri-Pane: (VT: 0.60*)
- 1 Coating on surface 2
- 1 Coating on surface 5
SunStable™ Low-E Glass
A balanced option suitable for various climates, it blocks 70%+ of UV rays.
Dual Pane: (VT: 0.58*)
- DF/UW: 2 Coatings on surface 3
- WW: 2 Coatings on surface 2
Tri-Pane: (VT: 0.53*)
- 2 Coatings on surface 2
- 2 Coatings on surface 5
SunResist™ Low-E Glass
Designed for sunnier climates, it blocks over 90% of UV rays while keeping interiors cool.
Dual Pane: (VT: 0.54*)
- DF/UW: 3 Coatings on surface 3
- WW: 3 Coatings on surface 2
Tri-Pane: (VT: 0.49*)
- 3 Coating on surface 2
- 3 Coatings on surface 5
HeatSave™ Interior Low-E Coating
Available only in tri-pane configurations, this coating reflects heat back indoors, enhancing comfort in colder climates.
Tri-Pane Only: Adds a coating on surface 6
- SunFlow™ VT: 0.57*
- SunStable™ VT: 0.51*
- SunResist™ VT: 0.46*
Tempered Glass: For Safety and Durability
Tempered glass is heat-treated to be stronger and safer than standard glass. When broken, it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards.
Key Benefits:
- Safety: Required by building codes for windows near floors, doors, or in bathrooms.
- Durability: Withstands impacts better than regular glass.
- Peace of Mind: Ideal for homes with children or high-traffic areas.
Tinted Glass: Enhancing Privacy and Reducing Glare
Tinted glass offers subtle coloration to reduce glare and improve privacy while maintaining natural light transmission.
Options to Consider:
- Grey Tinted: A sleek, modern option that reduces glare and enhances privacy.
- Rain Tinted: Textured for added privacy and a decorative touch.
- Sandblasted Obscured: A frosted appearance that diffuses light while obscuring visibility.
- Pinhead Obscured: Classic privacy glass with a subtle texture.
Key Benefits:
- Privacy: Blocks visibility while allowing light to filter through.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Adds a decorative element to your windows.

Factors to Consider
Energy Efficiency
The right glass can significantly impact your energy consumption. For colder climates, opt for Low-E coatings like SunFlow™ or HeatSave™ to maximize heat retention. In sunnier regions, SunResist™ Low-E glass helps reflect solar heat and reduce cooling costs.
Safety and Building Codes
In areas where safety is a concern—such as near floors, staircases, or bathrooms—tempered glass is essential to meet building codes and provide added protection.
Privacy and Aesthetics
If privacy is a priority, consider tinted or obscured glass options like sandblasted or rain glass. These styles also add a decorative touch to your windows, enhancing your home’s aesthetic appeal.
Balancing Visible Transmittance (VT)
- High VT: Ideal for colder climates to maximize passive solar heating.
- Low VT: Suitable for warmer climates to limit heat and glare.

Making Your Decision
When selecting glass for your windows, consider your climate, energy goals, safety needs, and aesthetic preferences. Products like the JWC8500 series offer customizable solutions that combine advanced Low-E coatings, tempered safety options, and stylish privacy glass to meet your specific requirements.
By understanding the benefits of different glass types and how glazing surfaces and VT influence performance, you can ensure your windows provide the perfect blend of energy efficiency, comfort, and style.
Stay tuned for our next article, where we’ll explore the sash and its impact on window functionality and performance!
Explore Related Posts












